Synchronous vs Induction Motors: Key Differences Explained

Synchronous vs Induction Motors: Key Differences Explained
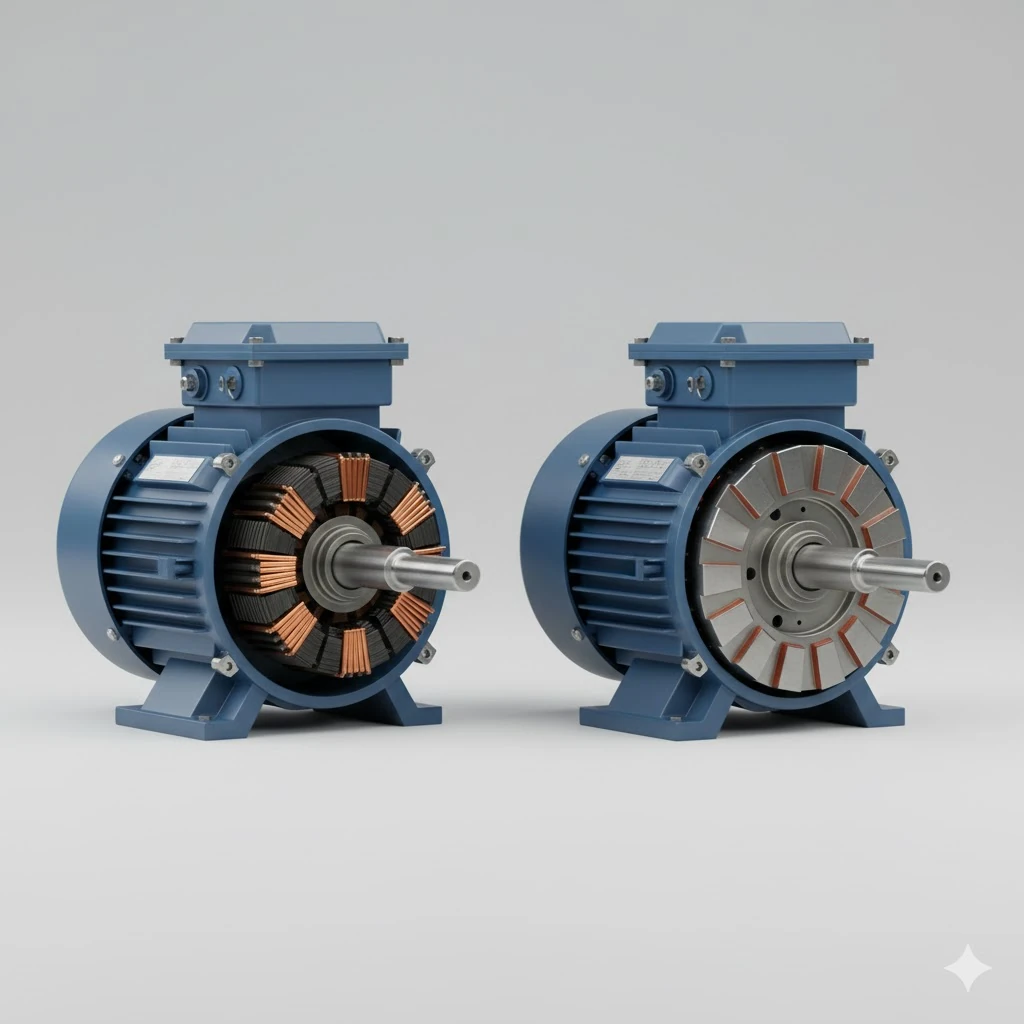
Electric motors in industry are broadly classified into two main types: induction motors and synchronous motors. While induction motors dominate most industrial applications, synchronous motors play a crucial role in precision and high-efficiency systems. Understanding the differences helps engineers select the right motor for performance, reliability, and energy usage.
1. Working Principle
- Induction Motor: The rotor rotates at a speed slightly less than synchronous speed due to slip. Current is induced in the rotor via electromagnetic induction.
- Synchronous Motor: Rotor rotates exactly at synchronous speed. Requires external excitation (DC supply or permanent magnets) to lock into synchronism.
2. Speed Characteristics
- Induction Motor: Speed varies with load due to slip; ideal for applications where small speed fluctuations are acceptable.
- Synchronous Motor: Constant speed regardless of load; perfect for precision or timing-critical applications.
3. Efficiency & Power Factor
- Induction Motor: Good efficiency but lower power factor at partial loads.
- Synchronous Motor: Very high efficiency; power factor can be controlled (leading, lagging, or unity).
4. Construction Differences
- Induction Motor: Simple, rugged construction. No slip rings in squirrel-cage designs.
- Synchronous Motor: Contains slip rings (in wound rotor types) or permanent magnets. More complex but offers better performance stability.
5. Applications
- Induction Motors: Pumps, fans, compressors, blowers, conveyors—general industry use.
- Synchronous Motors: Power plants, steel mills, cement plants, precision machines, large compressors, and applications requiring constant speed.
6. Cost & Maintenance
- Induction Motor: Lower cost, minimal maintenance, highly reliable.
- Synchronous Motor: Higher cost, requires excitation system, more complex maintenance.
7. Which One Should You Choose?
- Choose Induction Motor: For general-purpose, cost-effective, rugged applications.
- Choose Synchronous Motor: When constant speed, high efficiency, or power factor correction is required.
CG Power Solutions
CG Power offers both induction and synchronous motors with high efficiency, rugged construction, and a wide range of configurations. Bombay Engineering Syndicate provides end-to-end support for selection, sizing, and installation based on your application.
Final Thoughts
Both motor types have important roles in industry. While induction motors are the workhorses of most applications, synchronous motors deliver exceptional efficiency and constant-speed performance. Selecting the right type ensures reliability, energy savings, and long-term operational stability.
Contact us today for guidance on selecting the right motor technology.
By: Manish Chandrani; +919825014977